Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are revolutionizing industries by providing tools for mapping, spatial analysis, and decision-making based on geographic data. From agriculture and urban planning to transportation and disaster management, GIS technologies are indispensable for collecting, managing, and analyzing geographic information. However, while the benefits of GIS are undeniable, solution providers in this field face a range of challenges that can hinder the development, deployment, and adoption of their technologies. As the demand for advanced geospatial solutions grows, these challenges need to be addressed to ensure that GIS remains an effective tool for industries worldwide. In this article, we explore the key challenges faced by GIS solution providers and how they can overcome them.
1. Data Complexity and Quality Issues
One of the major challenges for GIS solution providers is the complexity and quality of the data they work with. Geographic data comes from multiple sources, such as satellite imagery, GPS devices, sensors, and surveys. This data can be diverse in format, scale, and accuracy, making it difficult to manage and integrate into a cohesive system. Data quality is another issue. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to flawed analysis and decision-making, undermining the credibility of GIS solutions. Ensuring high-quality, up-to-date geographic data is essential, but achieving this requires significant investment in data collection, validation, and maintenance. To address this challenge, solution providers must invest in advanced data management tools that can handle the complexity of geospatial data. They must also establish processes for data validation and updating, ensuring that their clients are working with reliable, accurate information.
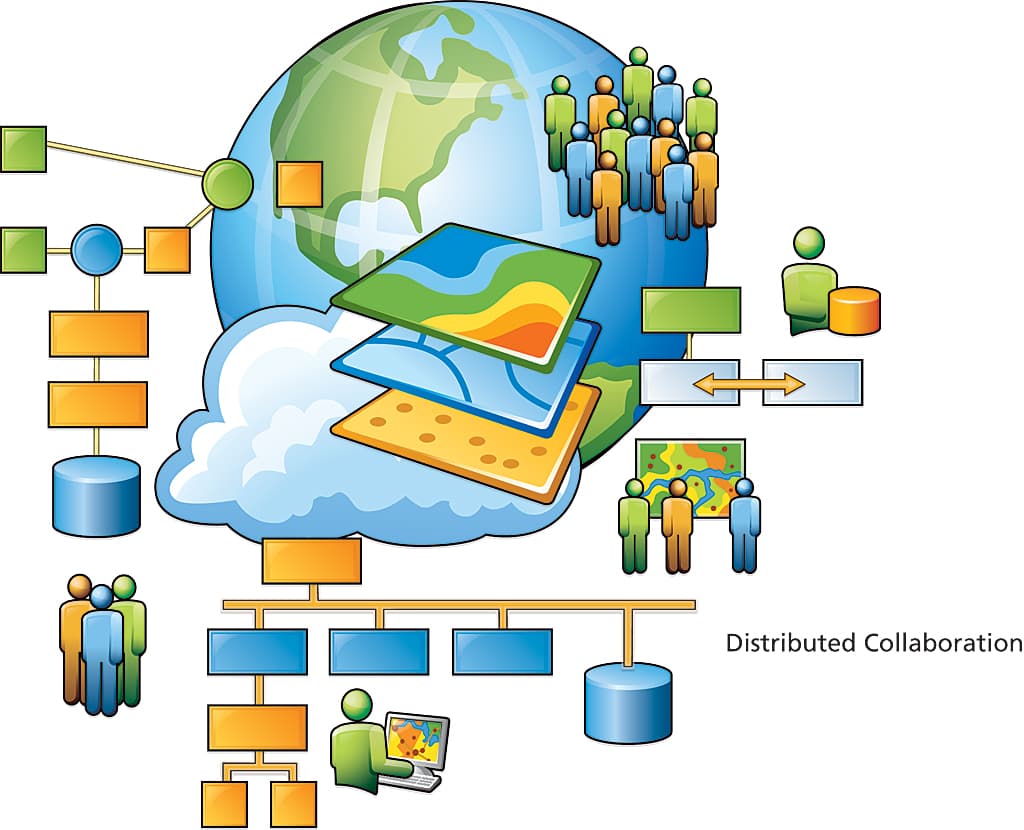
2. High Costs of GIS Technology
Implementing GIS solutions can be expensive, particularly for smaller businesses or organizations with limited budgets. The cost of GIS software, hardware (such as high-precision GPS devices), and data acquisition can quickly add up. Additionally, many GIS systems require skilled personnel to operate and maintain them, adding to the overall cost. This financial barrier limits the accessibility of GIS technology to large corporations or government agencies, while smaller organizations struggle to adopt these solutions. As a result, GIS solution providers face the challenge of making their products more affordable without sacrificing quality. One way to overcome this challenge is by offering flexible pricing models, such as subscription-based services or tiered pricing based on the size of the organization. Additionally, cloud-based GIS solutions, which reduce the need for costly hardware and infrastructure, can help make GIS technology more accessible to a broader range of users.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Many organizations rely on a wide variety of systems for managing their data and operations, from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to customer relationship management (CRM) software. Integrating GIS solutions with these existing systems can be a significant challenge, as it often requires custom development and technical expertise. For GIS solution providers, ensuring seamless integration with other software systems is crucial for enhancing the value of their products. Clients need the ability to incorporate spatial data into their existing workflows without disrupting their operations. This requires GIS providers to offer solutions that are flexible and compatible with a range of technologies, such as databases, cloud platforms, and third-party applications. To tackle this challenge, GIS providers should focus on developing open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and other integration tools that allow their solutions to connect easily with existing software. By enabling interoperability, they can help organizations make the most of their GIS investments.
4. Lack of Skilled Personnel
While GIS technology is powerful, it often requires skilled professionals to operate and interpret the data effectively. However, there is a shortage of trained GIS specialists in many regions, which limits the adoption of these solutions. Without the right expertise, organizations may struggle to utilize GIS tools to their full potential, leading to suboptimal results. For GIS solution providers, this shortage of skilled personnel poses a challenge in terms of product adoption and customer satisfaction. Organizations that lack in-house expertise may be reluctant to invest in GIS technology, fearing that they won’t be able to use it effectively. To address this issue, GIS providers can offer training programs, certifications, and user-friendly interfaces that make it easier for non-specialists to use their tools. Additionally, solution providers can offer managed services or consulting to help organizations get the most out of their GIS investments without needing to hire dedicated staff.
5. Security and Privacy Concerns
GIS solutions involve the collection and analysis of sensitive geographic data, which can raise concerns about security and privacy. For instance, GIS data used in industries such as defense, transportation, or public safety may contain confidential information that needs to be protected from unauthorized access or cyberattacks. As the use of GIS expands, the need for robust security measures becomes even more critical. GIS solution providers must ensure that their products are equipped with advanced security features to protect sensitive data, such as encryption, access controls, and secure data transmission protocols. To overcome these challenges, providers need to stay updated on the latest cybersecurity threats and continually invest in security enhancements for their products. They must also educate their clients on best practices for data protection and ensure that their systems comply with relevant regulations and standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for data privacy in the European Union.
6. Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Advancements
The pace of technological advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and remote sensing is rapid, and GIS solution providers must constantly innovate to keep up. These technologies have the potential to enhance GIS capabilities by enabling more advanced data analysis, real-time monitoring, and predictive modeling. However, staying ahead of the curve requires significant investment in research and development (R&D). For smaller GIS solution providers, this can be a daunting task, as they may lack the resources to invest in cutting-edge technology. As a result, they risk falling behind their competitors who are quick to adopt new advancements. To address this challenge, GIS providers can form partnerships with technology companies, research institutions, or government agencies to share knowledge and resources. By collaborating with others, they can stay at the forefront of innovation while reducing the financial burden of R&D.
GIS solution providers face several challenges, including data complexity, high costs, integration issues, lack of skilled personnel, security concerns, and the need to keep up with technological advancements. Despite these challenges, the demand for GIS technology continues to grow, driven by its ability to provide valuable insights and improve decision-making across industries.
By addressing these challenges through innovation, flexible pricing, and collaboration, GIS solution providers can continue to expand their reach and help organizations harness the power of geographic data for a better, more efficient future.






[…] digital4design.comwritesonic.cominsightland.orgdigitalstrike.comwalkersands.comforbes.comsamanthanorth.comfoundationinc.comgravitywrite.comboomcycle.comseo.comicebergwebdesign.comemetdigital.comseosandwitch.comblog.hubspot.comsearchengineland.commordorintelligence.comblog.googlepewresearch.orgemarketer.comnngroup.combacklinko.comschema.orggartner.comwodo.digitalarxiv.orgbrandwell.aigenerative-engines.comfirstpagesage.comanalyticsinsight.netdatastudios.orgbaytechconsulting.comzeo.orgGartner CMO Survey Reveals Marketing Budgets Have Dropped to 7.7% of …The State of Marketing Report 2024 – Influencer Marketing Hub2024 Annual Marketing Report – NielsenMarketing Spend Outlook 2024 – Plural StrategyMarketing Budget Trends for 2024 – GDS GroupDigital Marketing Statistics 2024 By Trends and Facts2025 Marketing Budget Trends – Report & Expert Insights2025 Marketing Budget: Insights from 11,000+ CMOsThe 2025 State of Marketing & Trends Report135 SEO Statistics for 2025The State of Marketing Spend 2025 – Benchmarks & trendsAI marketing statisticsAI Marketing: Must-Know Statistics for Early 2024AI Statistics For 2024The CMO SurveyCMOs Plan Big Investments In AI For The Next Three YearsThe CMO Survey ResultsHubSpot Annual Reports2024 HubSpot Annual ROI ReportState of HubSpot Report 2024Adobe US 2024 Quarterly ForecastHubSpot State of MarketingSalesforce’s 9th State of Marketing Report Highlights AI and Data TrendsAdobe sales & marketing expense 2010-2024 – StatistaAdobe 2024 Digital Trends ReportThe CMO Survey: Marketers Spend on New Technologies as They Battle Usage and ImpactHubSpot Marketing StatisticsArtificial intelligence (AI) use in marketing – statistics & factsThe 2025 State of Marketing Report by HubSpotSociobitsDigital Society PressWeForumEDRMTyn MagazineEconomic TimesMSNMashableArs TechnicaThe AI InsiderCtolWorld MagzineYouTubeSearch Engine JournalThe VergeCEO Today MagazineSearch Engine LandYahoo FinanceMercury NewsMSNDesignRushAxiosB17NewsNasdaqMicrosoft Corporate Blogsvcioglobal.comThe Vergegalaxy.aigeeky-gadgets.comquotesoftheday.orgNational TechnologyFusion ChatThe VergeOpenAICRNNVIDIAMSNHPCwireMacRumors9to5MacMacTrastTom’s GuidePhoneArenaTechSpotEntrepreneurFortunedarioamodei.comBloombergTranscript of the U.S. AI Leadership InterviewForbesFuturo ProssimoAxiosFortuneAlphabet Q4 EarningsUptrends.AIYahoo Finance LiveGoogle BlogMintThe VergeAnalytics InsightInvestopediaFusionChatMeta for DevelopersCNNThe AI InsiderCRNGartner Predicts Search Engine Volume Will Drop 25% by 2026, Due to AISearch Engines in 2026: AEO vs. GEO vs. SEO – onedotm.comWill traffic from search engines fall 25% by 2026? – Search Engine LandHow Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Rewrites the Rules of Search – a16zGEO vs. SEO: Understanding the Future of Search – seo.comWill Search Engine Traffic Really Drop 25% by 2026, As Gartner Predicts? – LinkedInTraditional Search Forecast To Fall 25% By 2026: Gartner – MediaPostForrester Predictions 2025GenAI in Numbers – Gartner and Forrester PredictionsAI Market Size and GrowthAI Statistics and TrendsIndustry Outlook and Investment TrendsThe economic potential of generative AI: Forecasts of McKinseyThe age of Generative AI: Unveiling the next frontier of digitalThe State of AI: Global surveyGlobal Digital Ad SpendingTraditional Search Will Decline by 25% by 2026 Because Of AI ChatbotsWill Search Engine Traffic Really Drop 25% by 2026?Gartner predicts 25% dip in search engine volume by 2026 due to AIStatista: U.S. marketing spending changes 2012-2026EMarketer: 2026 worldwide B2B digital ad spend forecastNorthstar Creatives: Predictions for 2026 and beyondGoodway Group: Digital marketing budget allocation strategiesWhat the data says about AI, search, and buyer behaviorAI Search Is Reshaping Consumer Behavior And Brands Must AdaptThe B2B Buyer Journey ResearchForrester’s AI Predictions 2024: What Marketers Need to KnowIDC Resource Center – Generative AIIDC’s Worldwide AI and Generative AI Spending – Industry OutlookIDC Worldwide AI and Generative AI Spending GuideIDC Press Release on AI Spending ForecastDeloitte Global’s 2025 PredictionsGlobal Marketing Trends | Deloitte USModernize marketing to accelerate growth | Deloitte DigitalEmbracing the Future: Marketing Trends for 2025-2026 – LinkedInGlobal Marketing Trends in the Digital Age – WSJPwC’s Global Artificial Intelligence StudyAdopting AI Will Make Or Break Businesses, Prediction Report FindsAI as a strategic game-changer88% of US firms to increase AI budgets80+ Up-to-Date AI Statistics for 2025PwC Survey on AI budgetsTop 10 GIS Tools to Watch in 2025 – atlas.coTop 5 GIS Software in 2025 – geodatainsights.com30 Best GIS Software Applications – GIS GeographyTop 5 Geotechnical Engineering Software 2025 – aldoa.comBest GIS Software 2025 – softwarereviews.comhttps://dev.to/czmilo/geo-vs-seo-comparative-analysis-report-from-search-optimization-to-ai-era-marketing-transformation-3k37https://gravitywrite.com/blog/geo-vs-seohttps://www.icebergwebdesign.com/2025/02/geo-vs-seo/https://boomcycle.com/blog/seo-vs-geo-understanding-the-key-differences/https://www.elsner.com/geo-vs-aeo-vs-seo-comparison-guide/https://www.geekscodes.com/2025/06/seo-vs-aeo-vs-geo-vs-sxo-vs-aio.htmlhttps://zerogravitymarketing.com/blog/geo-vs-seo/https://lseo.com/generative-engine-optimization/geo-vs-seo-key-differences-why-they-both-truly-matter/https://kingy.ai/blog/generative-engine-optimization-navigating-the-new-frontier-of-digital-visibility-in-2025/https://deloitte.com/us/en/what-we-do/capabilities/applied-artificial-intelligence/content/state-of-generative-ai-in-enterprise.htmlhttps://seosandwitch.com/generative-engine-optimization-stats/https://blog.darwinapps.com/blog/9-best-generative-search-optimization-tools-for-2025https://writesonic.com/blog/generative-engine-optimization-toolsReal-World GEO Wins: Case Studies from Early AdoptersGEO Case Study: SaaS Company To Scale LLM Traffic With GEOCase Study: Maximizing ROI with Beacon Technology and GeoAs AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO To GEO – ForbesWhat’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) & How To Do ItGeo-Integrated Retail Case StudyThe SEO to GEO Revolution: How AI Is Rewriting Search Strategy in 2025GEO Master Blueprint – Udemyhttps://www.fusegis.com/5-challengeshttps://scholarworks.umass.edu/bitstreams/efe5a02d-e2d7-448e-a2e5-a178766b8315/downloadhttps://spyro-soft.com/blog/geospatial/strategies-to-conquer-gis-implementation-challengeshttps://theciomedia.com/challenges-faced-by-gis-solution-providers-navigating-the-complexities-of-ge…https://www.geospatialworld.net/blogs/challenges-implementation-geospatial-technologies/https://ellipsis-drive.com/blog/top-4-challenges-in-gis-implementation/https://linkedin.com/pulse/barriers-spatial-data-gis-implementation-we-making-uu9ufThe Essential Guide to GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) Tools for Your Website in 2025GEO in 2025: The Smartest Way to Dominate AI SearchWhat is Generative Engine Optimization: The Complete Guide 2025GEO: The Complete Guide to AI-First Content Optimization 2025GEO Tools: The Ultimate Guide to Generative Engine Optimizationhttps://tuyadigital.com/generative-engine-optimization-analytic-tools/https://contently.com/2025/05/25/top-10-tools-for-generative-engine-optimization-in-2025/https://usehall.com/guides/generative-engine-optimization-toolshttps://sourceforge.net/software/generative-engine-optimization-geo/https://addlly.ai/blog/generative-engine-optimization-tools/https://sellm.io/post/best-generative-search-optimization-toolsfirstpagesage.com: AI Search Optimization: Strategy and Best Practices for 2025.techcommunity.microsoft.com: RAG Best Practice With AI Search.reforge.com: Optimizing for AI Search and Discovery.seomator.com: AI Search Optimization in 2025.servicenow.com: AI Search Expert-Recommended Practices.nav43.com: How to Optimize for AI Search in 2025.taksudigital.com: Generative Engine Optimization Guide.GEO vs SEO Comparative Analysis Report: From Search Optimization to AI …SEO vs AEO vs GEO vs SXO vs AIO 2025 Explained – geekscodes.comGEO vs SEO: Full Overview of Engine OptimizationGEO vs SEO in 2025: Key Differences, Optimization Tips & ToolsHow Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Rewrites the Rules of Search […]
Comments are closed.